Sodalime is a chemical absorbent commonly used in anaesthesia systems to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from exhaled breath. It is often used with mechanical ventilation to maintain a proper balance of gases during surgery.

The EtCO2 (end-tidal carbon dioxide) graph is a graphical representation of the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of a breath, which is measured during the respiratory cycle.
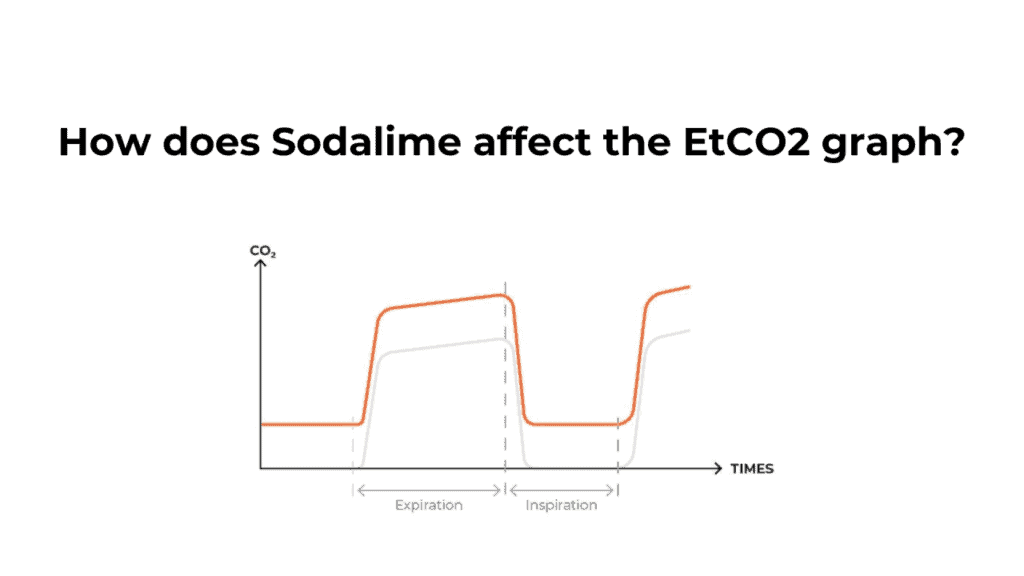
Sodalime absorbs CO2 from the exhaled breath before the patient inhales again. This absorption of CO2 is reflected in the EtCO2 graph.
Sodalime has a certain capacity to absorb CO2 gas. When it reaches its peak absorbing capacity, it needs to be replaced. Otherwise, the patient starts inhaling unabsorbed CO2 gas that he exhaled previously.
Due to this condition, the EtCO2 graph baseline changes.
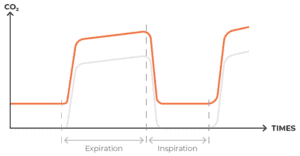
In the above image, the orange line shows exhausted Sodalime whereas the grey line depicts normal capnography waveform.
To sum up, the crucial function of EtCO2 in identifying depleted soda lime during anaesthesia underscores its significance in surgical environments.
References:
[1] Australian College of Veterinary Nursing (image) [Link]
—
[Click here] to learn more about “The World’s First Smart Capnometer”